The well mannered time period is “over-optimization.” However relying on the intention and extent, the blunt time period is “spam.” Both means, it’s a slippery slope to moving into the various search engines’ unhealthy graces.
How are you aware in case your content material is over-optimized? When your web site is flagged for a guide penalty. Google tells you by way of a message in Search Console. That’s the best-case situation, as there’s an issue to repair.
The worst-case situation is an algorithm penalty. You gained’t get a notification. You’ll see site visitors to the impacted pages drain away for no apparent motive. If there’s an algorithm replace, you’ll not less than have a date in your analytics to begin figuring out the underlying trigger. In any other case, you’ll surprise if the ways you’ve employed are out of favor, or if there’s another trigger that you simply’re lacking.
On this submit, I’ll handle 4 indicators that your content material may very well be over-optimized, risking a penalty or a rankings hit. Look at your content material skeptically. Take into consideration the way it seems to people, not search engines like google.
Hidden Content material
Exhibiting content material to search engines like google that guests aren’t meant to see is a violation of Google’s pointers in addition to most different search engines like google.
Right here’s an instance. This web page appears to be like superb till you click on on the “Extra Data” hyperlink within the footer. Then the primary portion of the web page is changed with content material that serves little function aside from to focus on “automobile rental” key phrases.
This web page incorporates content material for search engine bots however not people. Click on picture to enlarge.
Clicking the “Subsequent” button scrolls you thru a complete of 5 such screens, every focusing on a preferred key phrase phrase.
Technically, a customer might see this content material as a result of it’s triggered by a clickable hyperlink within the footer. Nonetheless, nobody would moderately click on that hyperlink, given its location, dimension, and label. It’s a transparent case of hidden content material.
In reality, the builders marketed their intent within the code, calling it “SEOPanel1” and declaring it as “PanelHidden.” It’s simple for a search engine advisor to seek out, and it might be simple for a search engine to detect both algorithmically or by a human, guide assessment.
Nevertheless it’s not at all times this reduce and dry.
Utilizing “hidden” within the supply code doesn’t essentially denote over-optimization. “Hidden” is often utilized in CSS as a reputable solution to regulate when menus, tabs, and accordion content material will and gained’t present. Ninety-nine % of the time, the phrase “hidden” doesn’t point out misleading website positioning ways.
Likewise, inserting “website positioning” within the code may be harmless. It’s typically a handy label for content material that was requested by the website positioning crew. For instance, the web page under incorporates respectable descriptive and related content material, despite the fact that the code round it screams that it’s for website positioning functions.
The phrase “website positioning” used as a label within the code might not reveal over-optimization. Click on picture to enlarge.
This web page doesn’t look like over-optimized. It goes on to listing tenting merchandise (maybe too aggressively) however ends with inspirational content material across the joys of tenting. If something, the corporate ought to label it in another way, maybe as “copy” or “content material” — not “website positioning” — however it’s a low precedence.
Key phrase Stuffing
Utilizing phrases and phrases merely for search engines like google and never for people known as “key phrase stuffing.”
Stuffing can occur in a single sentence, an extended piece of textual content, a heading, navigation, inside picture alt attributes — anyplace there may be textual content. It makes for awkward and unnatural studying.
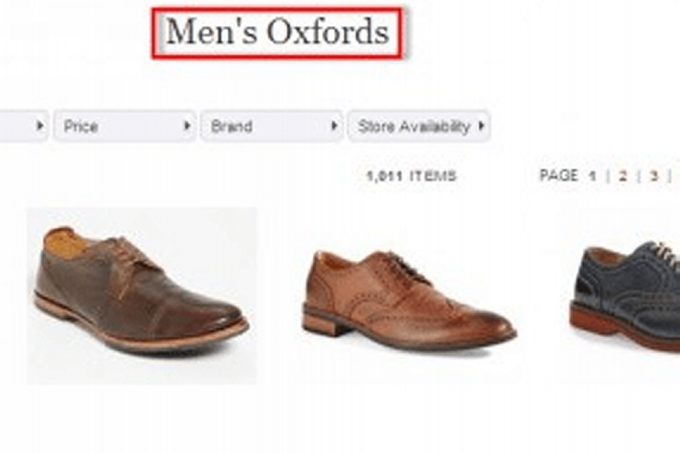
For instance, the block of textual content under is on the backside of an attire class web page incorporates the phrase “girls” 25 occasions. It’s paired with different phrases to make phrases — comparable to “girls’s sneakers” and “girls’s jackets.” It’s painful to learn.
This textual content incorporates the phrase “girls” 25 occasions. It’s painful to learn. Click on picture to enlarge.
Repetitive Pages
Carried out effectively, content material hubs can manage information to assist customers. Carried out deceptively, content material hubs exist just for website positioning, utilizing particular and overlapping key phrases.
The important thing, once more, is placing your self in guests’ sneakers. Is the content material helpful? Would a human learn it? Is it totally different from different pages on the positioning? If the reply isn’t any, it’s seemingly over-optimized.
Right here’s an instance from a payday loans web site. The web page presents three classes — “On-line Merchandise,” “Charges & Necessities,” and “On-line Companies.” Every class incorporates repetitive, redundant articles across the similar phrases and phrases. The tactic contains inner linking that’s separate from the positioning’s main navigation, which makes use of pure phrases and navigation.
These payday loans article titles all carefully relate to a selected key phrase phrase: “payday.” Click on picture to enlarge.
Under-the-footer Textual content
Something positioned exterior the boundaries of the positioning’s design, comparable to under the footer, is suspicious — particularly if it incorporates aggressive key phrases. If it’s content material you need guests to learn, embrace it inside the design of the web page. If not, it shouldn’t be in your web site.
Textual content under the footer is often an indication {that a} web page is over-optimized. Click on picture to enlarge.
The instance above is the house web page of a preferred web site. The textual content under the footer is the one content material aside from class photographs and hyperlinks. It contains 622 phrases and 18 hyperlinks with optimized anchor textual content. That’s sufficient content material for many articles and three-to-four occasions extra hyperlinks than a submit of that size ought to comprise.
Corporations that use this tactic typically argue that it’s working. On this case, the rankings point out that one thing is working, if not the over-optimized textual content. Nonetheless, Gary Illyes, a webmaster traits analyst with Google, had this to say about below-the-footer textual content: “Apparently, most loud, self-proclaimed ‘finest SEOs’ implement that after which they complain about being hit by some replace.”