For years title tags had been the first ingredient of natural search optimization. They helped Google match search queries to internet pages, they usually had been probably the most outstanding a part of result-page snippets, with the question in daring.
Titles stay essential for search engine optimisation. However loads has modified, and little is simple.
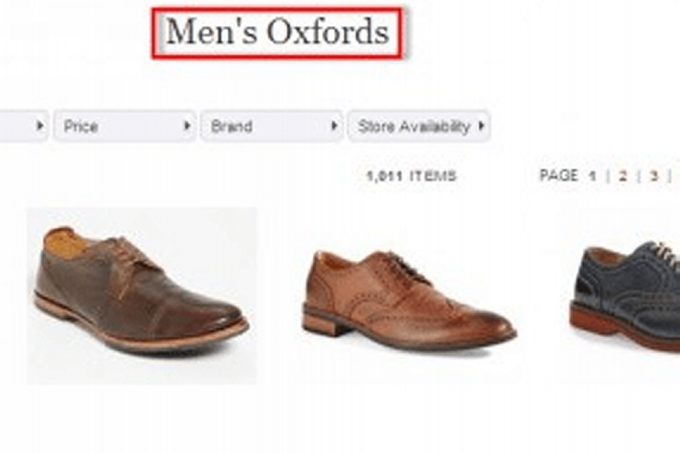
Google as soon as positioned the search question in daring textual content in title tags, as on this instance for “tag heuer.”
What Is a Title Tag?
A title tag is an HTML ingredient that ought to describe the web page’s objective in order that people and engines like google shortly perceive. It additionally seems because the title of a browser tab.
Title tags seem because the title of a browser tab, reminiscent of these 4 examples.
Google has slowly decreased the significance of title tags in search.
- Titles now not show the search question in daring throughout the snippet, attracting fewer clicks.
- Actual-match key phrases are much less essential, as Google typically makes use of synonyms and associated phrases when it understands the searcher’s intent.
- Google will typically rewrite titles within the search snippet.
Observe the screenshot under for the search question “mountain climbing trails clifton park.” Google interprets the question and gives outcomes for Saratoga Springs, close to Clifton Park. Furthermore, Google suggests another exercise (“operating” as a substitute of mountain climbing) and a synonym (“strolling”).
A couple of years in the past, an internet web page needed to include the precise question within the title tag to rank. No extra.
Google can discern a searcher’s intent and substitute outcomes with synonyms or comparable choices. On this instance, the question is “mountain climbing trails clifton park.” The outcomes included a close-by city and a comparable exercise.
Easy methods to Optimize Title Tags
Regardless of the adjustments, title tags assist Google perceive the web page and thus stay an essential search engine optimisation ingredient.
However Google’s use of titles isn’t as apparent.
As a substitute of matching the search question to phrases within the titles, Google can now perceive the which means of each the question and the title to match the searcher’s intent.
Hold titles brief, and don’t stuff key phrases. Google states in a weblog put up that it’s going to change the title if it’s too lengthy or over-optimized (i.e., filled with key phrases).
In any other case, compose a title as follows:
- Make it brief. Google doesn’t say how lengthy is simply too lengthy, however a title greater than 65 characters would truncate in desktop search outcomes. So protecting titles at that size or much less looks as if a good suggestion.
- Don’t stuff key phrases. Add key phrases within the title if it is sensible, which it typically does. However don’t embrace variations — reminiscent of plural and singular, or altering the order — which had been as soon as a regular search engine optimisation apply.
- Keep away from repetitive and boilerplate textual content. Large database-driven ecommerce websites typically generate automated titles. Be sure the phrases in these titles are informative (“iPhone 11 Case $6.99+”) and never repetitive (“Low cost Telephone Case | Cheap Telephone Case”).
Place the title tag on the web page. When searchers click on a search consequence, Google needs them to see the precise textual content on the following web page. So use the title tag prominently on the web page to guarantee searchers and scale back bounces.
Thus for title tags which are additionally H1 or equal headers on a web page:
- Google will probably preserve it as is,
- On-page engagement from searchers will probably enhance.
People, Not Algorithms
Google will do what’s finest for searchers. Genuinely useful titles discourage Google from rewriting them in snippets. Optimize for people, not algorithms. That’s the rule for contemporary search engine optimisation.